How to Cure Piles and Prevent Recurrence
- 5 min read

Dealing with the discomfort, itching, and pain of hemorrhoids can feel very exhausting. The constant itching, burning sensation, bleeding, and discomfort during bowel movements can interfere with your daily routine and make even simple activities stressful. Even after treatment, they can come back again and again if proper care isn’t taken, which makes the condition especially frustrating.
The good news is that with the right lifestyle changes, diet, and timely treatment, piles can be effectively managed and recurrence can be prevented. By understanding the causes and knowing how to cure piles and prevent recurrence, you can move from constant irritation to lasting relief.
Understanding Piles and Its Causes
Piles, also known as hemorrhoids, are swollen veins in the anal canal. They can cause discomfort, pain, itching, and sometimes bleeding during bowel movements. Piles are a common health problem, and many people in Nepal suffer from this condition due to lifestyle and dietary habits.
Piles develop when swollen veins in the anal canal experience increased pressure. Some of the major causes of piles are:
- Constipation: Straining during bowel movements increases pressure on the anal veins.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Sitting for long hours at work or at home reduces blood flow.
- Heavy lifting: Regularly lifting heavy objects increases abdominal pressure.
- Pregnancy: The growing uterus puts pressure on pelvic veins.
- Low-fiber diet: Lack of high fiber foods like fruits vegetables and whole grains causes harder stools.
- Obesity: Extra weight puts more pressure on anal veins.
- Alcohol and caffeine: Both can dehydrate the body and worsen constipation.
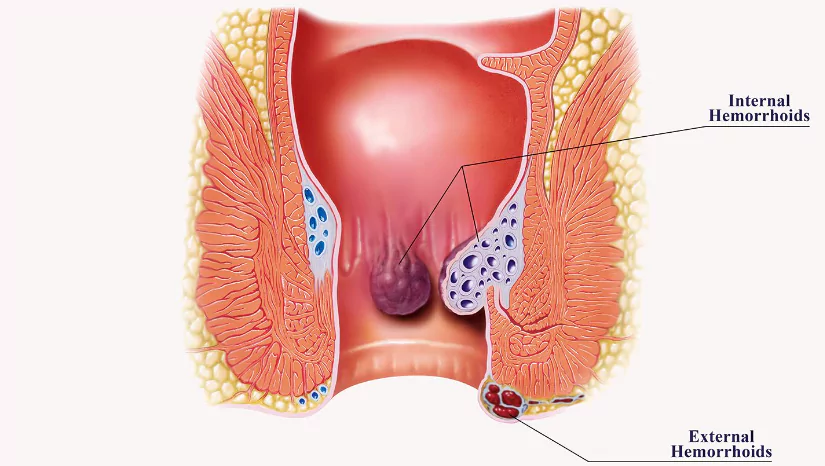
How to Cure Piles
Most mild to moderate piles can be managed at home using lifestyle changes, diet, and natural remedies. These steps relieve pain, reduce swelling, and prevent recurrence.
1. Eat a High-Fiber Diet
Diet plays a crucial role in piles treatment. A high-fiber diet softens stools, increases stool bulk, and reduces the need for straining during bowel movements, which is one of the main causes of piles. Some of the foods to eat in piles are:
- Fruits: Apples, papaya, pears, berries
- Vegetables: Spinach, pumpkin, carrots
- Whole grains: Oats, brown rice, whole wheat bread
Drinking plenty of water along with fiber is essential. Fiber absorbs water, and without adequate hydration, it can actually worsen constipation. Aim for 2–3 liters of water daily, unless advised otherwise by a doctor.
At the same time, it’s important to be aware of food to avoid in piles, as it may worsen the problem. These include spicy foods, fried and fatty foods, processed snacks, excessive dairy, and very low-fiber foods like white bread and pastries.
Additional tips:
- Gradually increase fiber intake to avoid gas or bloating.
- Limit alcohol and caffeine as they can dry stools and worsen piles.
2. Maintain Healthy Bowel Habits
Poor bowel habits are a major reason piles develop and keep coming back. Training your body for regular, strain-free bowel movements is essential for long-term relief. Healthy practices to maintain healthy bowel habits are:
- Go to the toilet as soon as you feel the urge.
- Avoid straining during bowel movements.
- Do not sit on the toilet for long periods. Long sitting can increase blood flow to anal veins.
- Using a footstool slightly elevates the knees and helps stool pass more easily.
Hygiene tips:
- Clean the affected area gently with water after bowel movements.
- Use damp toilet paper instead of dry toilet paper to avoid irritation.
- Avoid rubbing the area vigorously.
3. Relieve Pain and Reduce Swelling
Pain, itching, and swelling are common symptoms, especially in external piles. The following remedies can provide significant relief:
- Sitz bath: Sit in warm water for 10–15 minutes, 2–3 times a day. It relieves pain and reduces inflammation.
- Ice packs: Apply cold packs for 10 minutes to reduce swelling.
- Witch hazel: Natural astringent that can reduce itching and soothe the affected area.
- Aloe vera gel: Soothes irritation and speeds healing.
- Coconut oil: Moisturizes the skin and reduces inflammation.
Tip: Always gently push any protruding piles back inside the anal canal if recommended by a doctor.
4. Exercise and Stay Active
Regular physical activity improves digestion, prevents constipation, and enhances blood circulation, reducing pressure on anal veins. Recommendations include:
- Daily walking for 20–30 minutes
- Yoga poses like Malasana (yogic squat) or Pawanmuktasana
- Light stretching if you sit for long hours
Avoid:
- Heavy weight lifting
- Prolonged sitting or standing without breaks
If you have a desk job, stand up and walk for a few minutes every hour.
5. Avoid Habits That Worsen Piles
Preventing piles is easier when common triggers are avoided. Certain habits increase pressure on rectal veins and slow healing.
Preventing recurrence is easier if you avoid common triggers:
- Straining during bowel movements
- Sitting for long periods, especially on hard surfaces
- Excessive alcohol and caffeine intake
- Smoking, which affects blood circulation and healing
- Low-fiber diet and poor hydration
These habits reduce pressure on the swollen veins and help relieve pain naturally.
6. Stay Hydrated and Limit Irritants
Proper hydration keeps stools soft and supports overall digestive health. Dehydration is a major contributor to constipation and piles.
Hydration tips:
- Drink water consistently throughout the day
- Include fluids like coconut water, soups, and herbal teas
- Avoid excessive spicy foods, which can irritate the anal area
- Reduce intake of carbonated drinks and sugary beverages
Spicy, oily, and junk foods can worsen inflammation and should be consumed in moderation or avoided during flare-ups.
7. When Natural Remedies Are Not Enough: Medical Treatment
Sometimes home remedies are not sufficient. In some cases, piles become severe or recurrent and do not respond to home remedies. Medical intervention may then be necessary. Piles treatment in Nepal may include:
- Rubber band ligation: Minimally painful procedure that cuts the blood supply to the hemorrhoid, making it shrink.
- Infrared light therapy: Works for small internal hemorrhoids.
- Laser treatment: Highly precise, minimally invasive piles laser procedure, and associated with less pain and quick recovery.
- Surgery to remove severe piles: Needed for large or recurrent internal hemorrhoids or external hemorrhoids that do not respond to other treatments.
Digital rectal exams are used to check internal hemorrhoids and blood clots. Always consult a qualified doctor or a piles hospital near you for proper evaluation and treatment, especially if you experience heavy bleeding, severe pain, or symptoms lasting more than a few weeks.
Warning Signs to See a Doctor
Home remedies and diet can manage mild cases, but they aren’t always enough. Consult a doctor immediately if you notice:
- Persistent bright red blood in stool
- Severe pain or small lumps that do not improve
- Piles do not respond to home remedies
- Recurrent piles symptoms despite lifestyle changes
Early consultation at a trusted clinic ensures safe and effective treatment, which is minimally painful and reduces the risk of complications. At Clinic Neo, we are dedicated to providing the highest standard of care for piles patients in Nepal.
Conclusion
Piles are common but also manageable. Most piles cases respond well to lifestyle changes, diet, and natural remedies. Following a high fiber diet, drinking plenty of water, regular exercise, good bowel habits, and proper hygiene can relieve pain and prevent recurrence.
However, if piles persist, recur frequently, or cause significant pain or bleeding, timely medical care is essential. For severe or persistent cases, minimally invasive procedures like laser treatment may be required. Combining natural remedies, good habits, and timely medical care can cure piles, relieve pain, and prevent them from returning.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How do you cure piles fast?
Piles can be managed quickly with a combination of lifestyle changes and medical treatments. Increasing fiber intake, drinking plenty of water, taking sitz baths, and using over-the-counter creams or suppositories can reduce swelling and pain. In more severe cases, minimally invasive procedures like rubber band ligation or laser therapy may provide faster and permanent relief.
2. What are the main causes of piles?
Piles develop due to increased pressure in the rectal veins. Common causes include:
- Chronic constipation or diarrhea
- Straining during bowel movements
- Prolonged sitting, especially on the toilet
- Pregnancy (increased pressure on pelvic veins)
- Obesity
- Low-fiber diet
- Heavy lifting
3. Do piles go away naturally?
Mild piles can improve on their own with lifestyle changes, but persistent or severe piles usually need medical treatment. However, moderate to severe piles rarely disappear without treatment and may worsen over time if ignored, requiring medical interventions.
4. Are piles very serious?
Most piles are not life-threatening, but they can cause significant discomfort, bleeding, and itching. In rare cases, untreated piles can lead to complications such as anemia, thrombosed hemorrhoids, or prolapse, which may require surgical treatment.
5. How to cure piles 100%?
A complete cure usually involves a combination of medical procedures and lifestyle modifications. Procedures such as laser treatment can remove the piles, while long-term prevention requires a high-fiber diet, regular exercise, and avoiding straining during bowel movements.
6. What happens if piles are left untreated?
Ignoring piles can lead to worsening symptoms, including severe pain, bleeding, chronic irritation, and prolapse. In some cases, blood loss from chronic bleeding can cause anemia. Thrombosed piles may form, which are extremely painful and may require urgent surgery.
Our Recent Blogs
Pilonidal Sinus: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options

Effective Nepalese Home Remedies to Relieve Constipation
Have you ever felt that heavy, bloated sensation in your...

How to Cure Piles and Prevent Recurrence

Food to Avoid in Piles and What to Eat Instead
Have you ever felt that stinging discomfort or noticed blood...

Piles: Types, Symptoms, Causes and Treatment in Nepal
Piles are a common problem that can cause pain, discomfort,...

Best Laser Surgery for Piles, Fissures, & Fistula in Nepal
Best Laser Surgery for Piles, Fissures and Fistula – Your...
